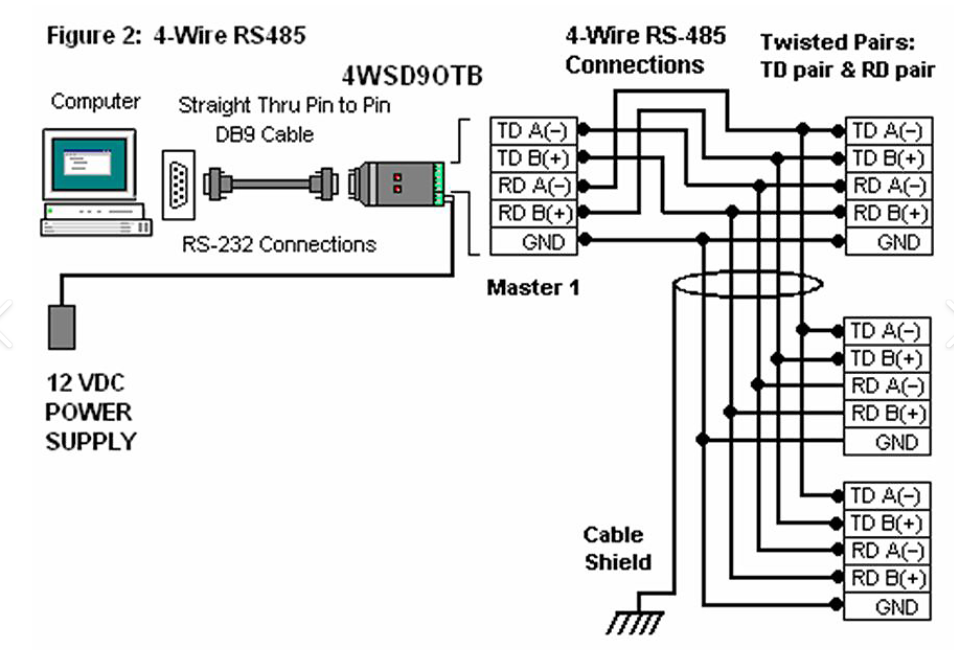
RS485 is one of the most widely used communication standards in industrial data acquisition, but many field issues come from incorrect wiring. Proper wiring ensures stable communication, fewer CRC errors, and long-distance reliability.
1. Use the Correct RS485 Wiring Topology
RS485 requires a daisy-chain (bus) structure:
- Master → device 1 → device 2 → … → final device
- Avoid star wiring
- Avoid branching
Correct topology reduces signal reflections and data loss.
2. Proper A/B Line Connections
RS485 uses two differential lines:
- A (−)
- B (+)
Always confirm:
- A connects to A
- B connects to B
- Do not mix polarity
Reversed wiring is the most common cause of Modbus RTU communication failure.
3. Enable Termination Resistors
At both ends of the bus, add:
- 120Ω termination resistors
- Optional bias resistors for signal stability
Termination reduces noise and prevents reflection on long-distance cables.
4. Choose Industrial-Grade Shielded Cable
For stable communication:
- Use twisted-pair shielded cable
- Connect shield to ground on one side only
- Avoid routing near high-voltage power lines
Good cabling improves noise immunity in harsh factory environments.
5. Keep the Baud Rate Realistic
Longer distance → lower baud rate.
Typical stable settings:
- 9600 bps
- 19200 bps
- 38400 bps
Higher speed may cause CRC errors over long cables.
6. Test With a Modbus Scanner Before Deployment
Use a PC or gateway tool to validate:
- Slave address
- Baud rate
- Parity
- Register map
Always confirm communication before integrating into your DAQ system.