RS485 interference troubleshooting focuses on identifying and mitigating noise sources that disrupt reliable serial communication in industrial environments.
Although RS485 is designed for high noise immunity, improper wiring, grounding, and network design can still cause communication instability.
In industrial data acquisition systems, communication reliability is as critical as sensor accuracy.
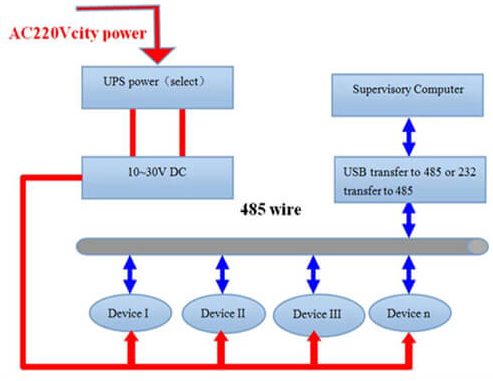
RS485 networks are widely used to connect industrial temperature sensors, pressure sensors, and flow sensors to PLCs, data loggers, and edge gateways.
These deployments often operate in environments with motors, inverters, relays, and high-current equipment, all of which can introduce electromagnetic interference.
Stable RS485 communication is therefore a foundational requirement for accurate data acquisition.
From a system perspective, RS485 interference issues typically stem from physical-layer design rather than protocol logic.
Differential signaling reduces common-mode noise but does not eliminate it entirely.
Multi-drop topologies increase susceptibility to reflections and signal degradation.
RS485 is commonly paired with the Modbus RTU protocol, which relies on strict timing and frame integrity, making it sensitive to noise-induced errors.
Several communication parameters influence noise tolerance.
Baud rate selection directly affects signal robustness over long distances.
Parity and data bit configuration must be consistent across all devices.
Timeout settings should account for network length and device response times.
Incorrect parameter configuration can amplify the impact of electrical noise.
RS485 is commonly used with industrial temperature sensors, industrial pressure sensors, and industrial flow sensors that rely on Modbus RTU for structured data exchange.
Noise issues affecting RS485 communication will therefore directly impact sensor data quality and system reliability.
These sensors are often distributed across large industrial sites, increasing exposure to interference.
Typical interference-related problems include CRC errors, intermittent timeouts, unstable readings, and complete communication loss during equipment startup.
Common root causes include missing termination resistors, improper grounding, shield connections at both ends, and cable routing near high-power lines.
Effective troubleshooting begins with physical inspection before protocol-level debugging.
RS485 interference troubleshooting is an essential engineering skill in industrial data acquisition projects.
Proper wiring, grounding, termination, and parameter configuration are necessary to maintain stable communication, especially when using Modbus RTU in multi-device networks.
Reliable data transmission ensures that sensor accuracy is preserved from the field layer to higher-level systems.