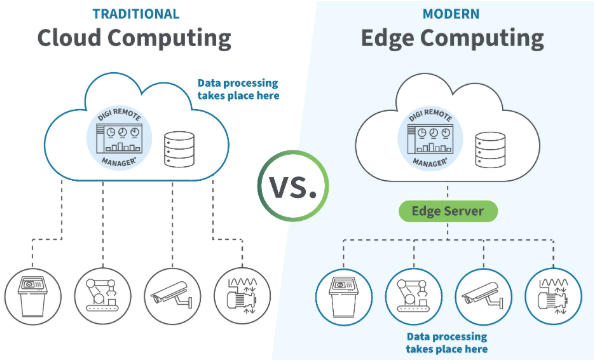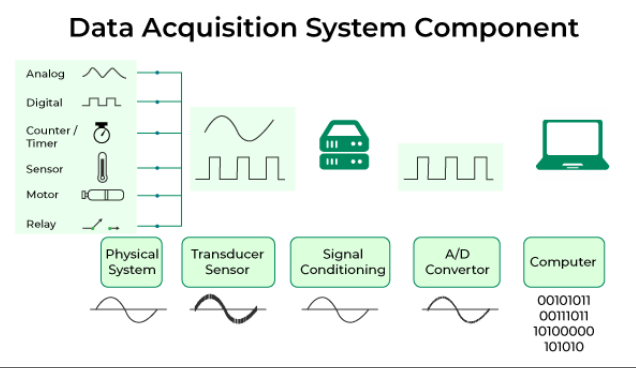
Selecting the right sensor is critical for building a reliable industrial data acquisition system. The wrong sensor leads to inaccurate data, unstable readings, and unnecessary maintenance costs. Here is a simple guide to choosing industrial-grade sensors.
1. Determine What You Need to Measure
The first step is defining your measurement target:
- Temperature
- Pressure
- Vibration
- Humidity
- Current / voltage
- Flow rate
- Position or speed
Each measurement requires a specific sensor type and accuracy range.
2. Check the Output Type
Industrial sensors usually support one or more of the following outputs:
- Analog 4–20mA / 0–10V
- RS485 / Modbus RTU
- Pulse output
- Relay / switch
- Ethernet / Modbus TCP
For web-based DAQ systems, Modbus RTU/TCP is the most scalable option.
3. Consider Environmental Conditions
Industrial environments can be harsh. Evaluate:
- Operating temperature
- Water or dust exposure (IP rating)
- Vibration resistance
- Electromagnetic interference
A sensor that looks good on paper may fail quickly in real factory conditions.
4. Match Sensors to Your DAQ Hardware
Your DAQ platform or IoT gateway must support the sensor’s interface:
- RS485 ports
- Analog input channels
- Digital input for pulse or relay
- Ethernet for TCP sensors
Good hardware compatibility reduces integration time and wiring complexity.
5. Ensure Calibration and Accuracy
For long-term stability:
- Use sensors with factory calibration
- Check accuracy tolerance
- Verify drift characteristics
- Choose brands known for industrial reliability
Accurate data leads to better decision-making and fewer process errors.