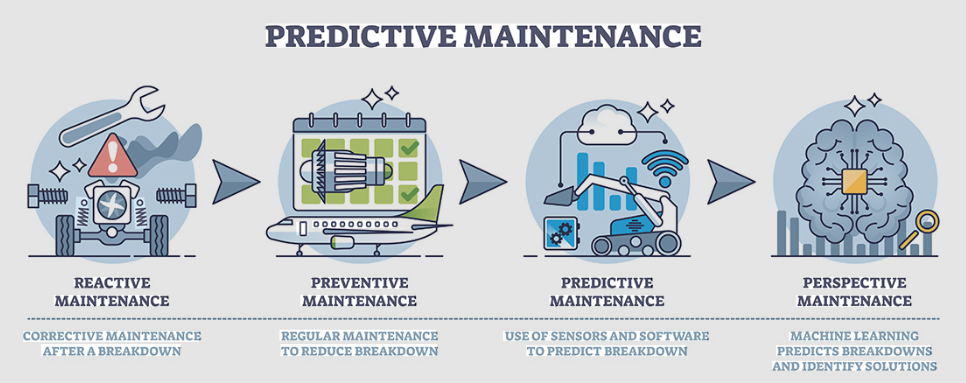
Predictive maintenance uses real-time and historical industrial data to detect early signs of equipment failure. Instead of reacting to breakdowns, factories can fix problems before they cause downtime.
1. What Is Predictive Maintenance?
Predictive maintenance analyzes data from:
- Vibration sensors
- Temperature sensors
- Current and power meters
- Runtime and cycle counters
The goal is to identify abnormal patterns that indicate wear or malfunction.
2. Why Predictive Maintenance Matters
Traditional maintenance strategies are either:
- Reactive — fix after failure
- Preventive — service on a fixed schedule
Both waste time and money. Predictive maintenance:
- Reduces unplanned downtime
- Extends equipment lifespan
- Lowers maintenance costs
- Improves production reliability
3. Key Data Used for Prediction
Common indicators include:
- Rising vibration levels
- Increasing motor temperature
- Abnormal current consumption
- Frequent start/stop cycles
- Trend deviations over time
These signals often appear weeks before failure.
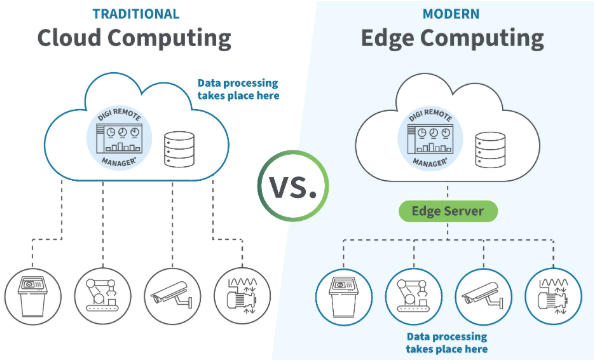
4. Role of DAQ and Edge Computing
Industrial DAQ systems and edge devices:
- Collect high-frequency sensor data
- Filter noise locally
- Calculate trends and thresholds
- Trigger early alarms
Only relevant insights are sent to the cloud.
5. From Monitoring to Prediction
With enough historical data, platforms can:
- Detect patterns
- Build baseline models
- Identify anomalies
- Support AI-based prediction
Predictive maintenance transforms maintenance from cost center to value creator.