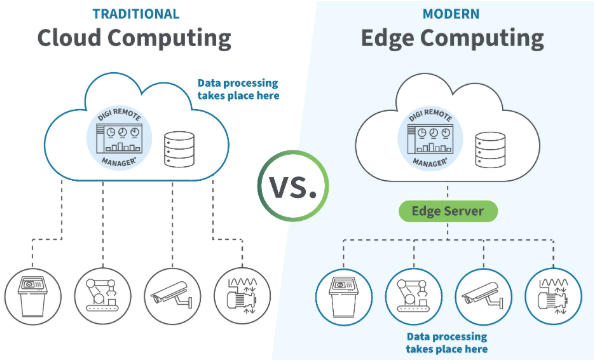
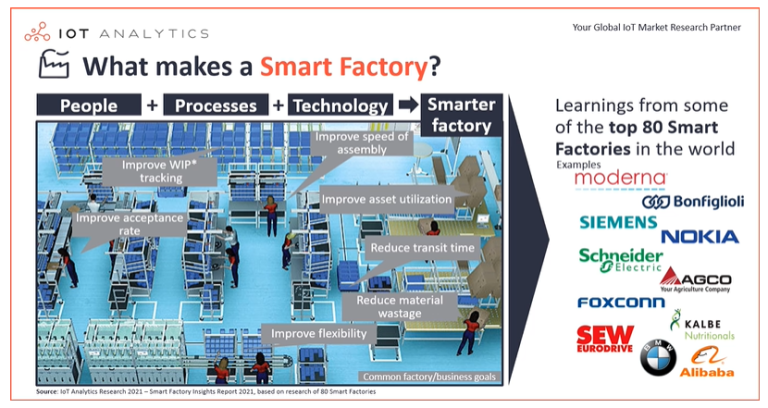
Energy is one of the largest operating costs in industrial facilities. With proper energy monitoring, factories can track consumption in real time, identify waste, and significantly reduce operating expenses.
1. What Is Industrial Energy Monitoring?
Industrial energy monitoring collects data from:
- Power meters
- Current transformers (CTs)
- Voltage sensors
- Smart energy meters
The data is then analyzed to understand how and where energy is used.
2. Why Energy Data Matters
Without accurate data, energy costs are invisible.
Energy monitoring enables:
- Detection of abnormal consumption
- Load analysis across machines
- Peak demand control
- Cost allocation by production line or department
This turns energy into a measurable and manageable resource.
3. Key Metrics to Monitor
Common energy KPIs include:
- Active power (kW)
- Energy consumption (kWh)
- Power factor
- Peak demand
- Load imbalance
Tracking these metrics helps optimize electrical systems and equipment usage.
4. How Energy Data Is Collected
Most energy monitoring systems use:
- Modbus RTU/TCP meters
- RS485 networks
- Industrial gateways
- Web-based dashboards
This allows real-time and historical analysis from a single platform.
5. Benefits for Industrial Facilities
- Lower energy bills through efficiency improvements
- Reduced carbon footprint
- Improved equipment health
- Support for ESG and compliance reporting
Energy monitoring is a fast-return investment for industrial digitalization.