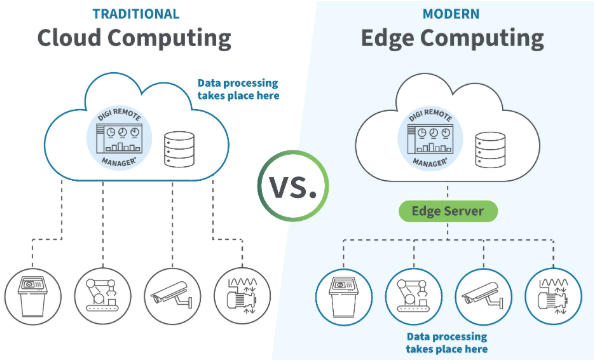
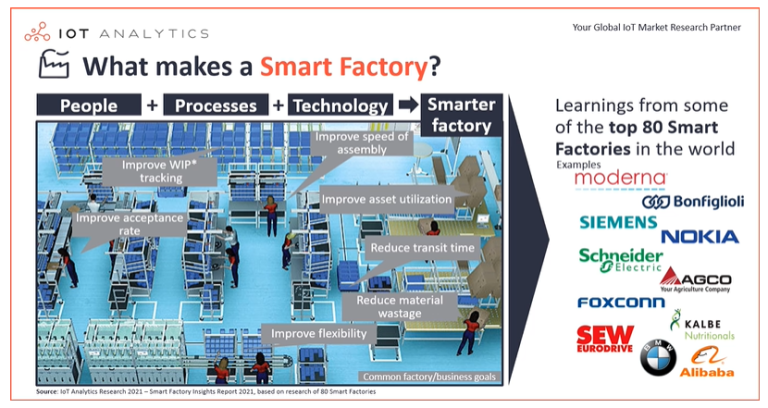
Real-time data is important, but historical data storage is what allows factories to analyze trends, optimize processes, and improve long-term performance. A reliable data storage strategy is a core part of any industrial data acquisition system.
1. Why Historical Data Matters
Storing industrial data enables:
- Trend analysis over days, months, or years
- Root cause analysis after failures
- Performance comparison across shifts or sites
- Compliance and reporting
Without historical data, valuable insights are lost.
2. Common Types of Industrial Data Stored
Industrial DAQ systems typically store:
- Sensor measurements (temperature, pressure, vibration)
- Machine status and runtime
- Energy consumption data
- Alarm and event logs
- Production metrics
This data forms the foundation for analytics and optimization.
3. Time-Series Databases for Industrial Data
Most industrial platforms use time-series databases because they are optimized for:
- High-frequency data
- Timestamp-based queries
- Fast aggregation and visualization
They allow efficient storage without excessive disk usage.
4. Data Retention Best Practices
To balance performance and cost:
- Store high-resolution data short-term
- Aggregate older data (hourly/daily averages)
- Define retention policies by data type
- Archive critical data for compliance
This ensures scalability as data volume grows.
5. Turning Stored Data into Value
Historical data supports:
- Predictive maintenance
- Energy optimization
- Capacity planning
- Quality improvement
- Continuous process improvement
Long-term data storage transforms industrial monitoring into strategic decision support.