Edge computing is transforming how factories collect, process, and use industrial data. Instead of sending all raw data to the cloud, edge devices process data locally, providing faster insights and more reliable operations.
1. What Is Edge Computing?
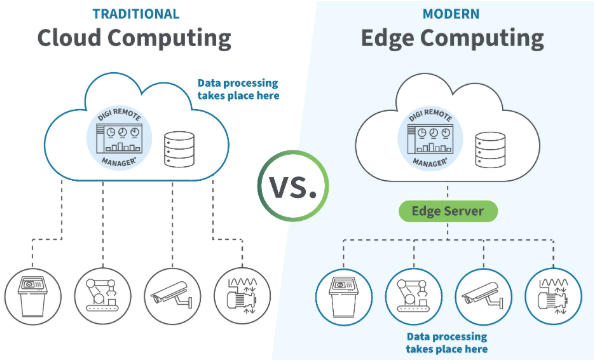
Edge computing means performing data processing near the machines, not in a remote server.
This is done using:
- IoT gateways
- Embedded controllers
- Industrial PCs
These devices run analytics locally, then send only useful results to the cloud or dashboard.
2. Why Edge Computing Matters in DAQ
Industrial systems generate massive data streams from:
- RS485 sensors
- PLCs
- Energy meters
- High-frequency vibration sensors
Sending everything to the cloud is slow and expensive.
Edge processing solves this by filtering and calculating data at the source.
3. Key Advantages
1. Lower Latency
Critical decisions—temperature alarms, machine faults, vibration spikes—must be detected instantly.
2. Reduced Network Costs
Bandwidth usage drops dramatically when raw data is processed locally.
3. Higher Reliability
Machines continue operating even if the internet goes offline.
4. Better Security
Less raw data leaves the factory floor, reducing cybersecurity risks.
4. Typical Edge Computing Functions
An industrial edge gateway can:
- Filter sensor noise
- Calculate averages, peaks, and thresholds
- Perform Modbus polling
- Trigger alarms
- Detect anomalies
- Pre-process vibration or energy data
This allows only meaningful results to be pushed to the cloud.
5. Where Edge Computing Is Essential
- Remote pumping stations
- Energy monitoring systems
- Multi-site industrial facilities
- Vibration/condition monitoring
- Manufacturing equipment with strict response time requirements
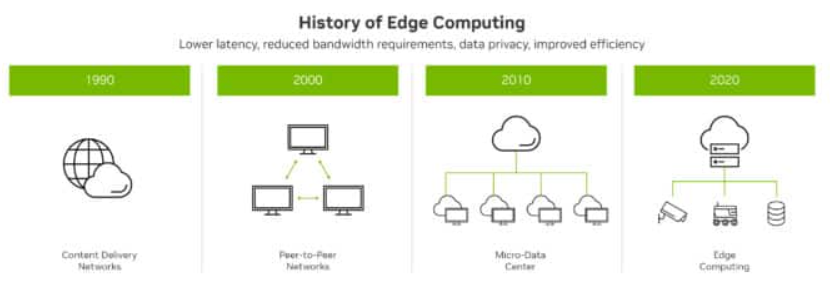
Edge computing is now the backbone of modern industrial IoT systems.